Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Markina, Irina
2017.
Analytic, Algebraic and Geometric Aspects of Differential Equations.
p.
89.

Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
We prove that the fundamental solutions of Kohn sub-Laplacians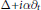 $\Delta +i\alpha {{\partial }_{t}}$ on the anisotropic Heisenberg groups are tempered distributions and have meromorphic continuation in α with simple poles. We compute the residues and find the partial fundamental solutions at the poles. We also find formulas for the fundamental solutions for some matrix-valued Kohn type sub-Laplacians on
$\Delta +i\alpha {{\partial }_{t}}$ on the anisotropic Heisenberg groups are tempered distributions and have meromorphic continuation in α with simple poles. We compute the residues and find the partial fundamental solutions at the poles. We also find formulas for the fundamental solutions for some matrix-valued Kohn type sub-Laplacians on 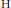 $\text{H}$-type groups.
$\text{H}$-type groups.